Importance of Coulomb’s law
When a charge is stationary then only the electric force acts on it. Which was discovered by Coulomb. Therefore it is also called Coulomb force.When a charge is stationary then only the electric force acts on it. Which was discovered by Coulomb. Therefore it is also called Coulomb force.
Coulomb’s law is true for very large distances to very small distances and even atomic and nuclear distances.
Therefore, this law not only helps in explaining the forces acting between charged objects due to which the electrons of an atom flow with its nucleus to form an atom.
Two or more atoms flow together to form molecules and form liquids. Most of the forces we experience in our daily life which are not gravitational forces are electrical forces.
Electrostatic force at a point due to continuous charge distribution,
There are three types of continuous charges,
1. Linear charge distribution
2. Surface charge distribution
3. Volume charge distribution
1. Linear charge distribution
Let a thin wire of length L be uniformly charged. The linear charge density on the wire is λ.
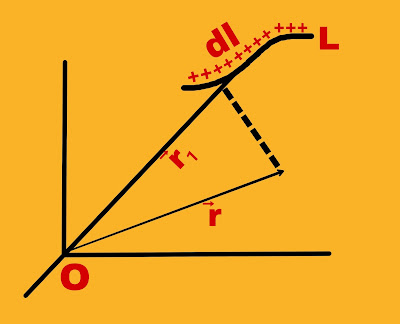
This linear charge distribution can be considered to be made up of microscopic charge segments.
If a microscopic element is section dl and the charge associated with it is dq, then
Therefore,
λ=dq/dl
dq=λ.dl
If the position vector of this section relative to the origin point O is →r₁ and the position vector of point P relative to the origin O is →r and the positive test charge qₒ at point P is the line, then the positive test charge on qₒ due to dq charge is total electric force,
2. Surface charge distribution
If charge is continuously distributed on a surface whose surface charge density is σ, then the charge related to the infinitesimal surface area ds of the surface is
dq = σ.ds
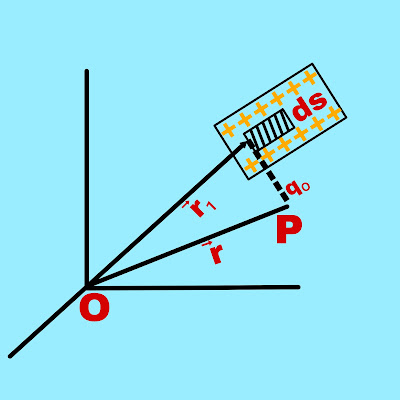
Let there be a point P whose positive test charge is qₒ, the position vector of point P relative to the origin point O is →r. The position vector of the surface element ds relative to point O is →r₁.
Therefore, the total electric force acting on a positive test charge qₒ placed at point P due to charge dq on the surface element ds is
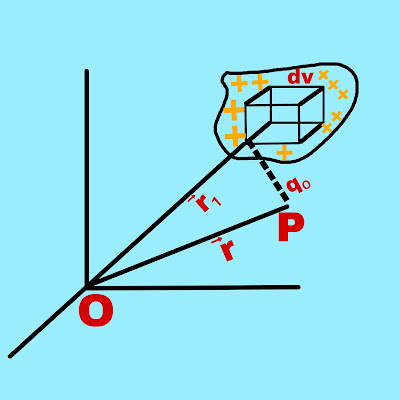
3. Volume charge distribution
If the charge is continuously distributed on a volume whose volume charge density is ρ, then the charge related to the smallest volume dv,
Suppose there is a point P at which the positive test charge is qₒ. The electric force due to volume charge distribution at this point P has to be calculated. The position vector of point P relative to point O is →r and the position vector of infinitesimal volume dv relative to point O is →r₁.
Therefore, the total electric force acting on a positive test charge qₒ placed at point P due to charge dq on the volume element dv is,



[…] Importance of Coulomb’s law —- […]