Principle
According to this principle,
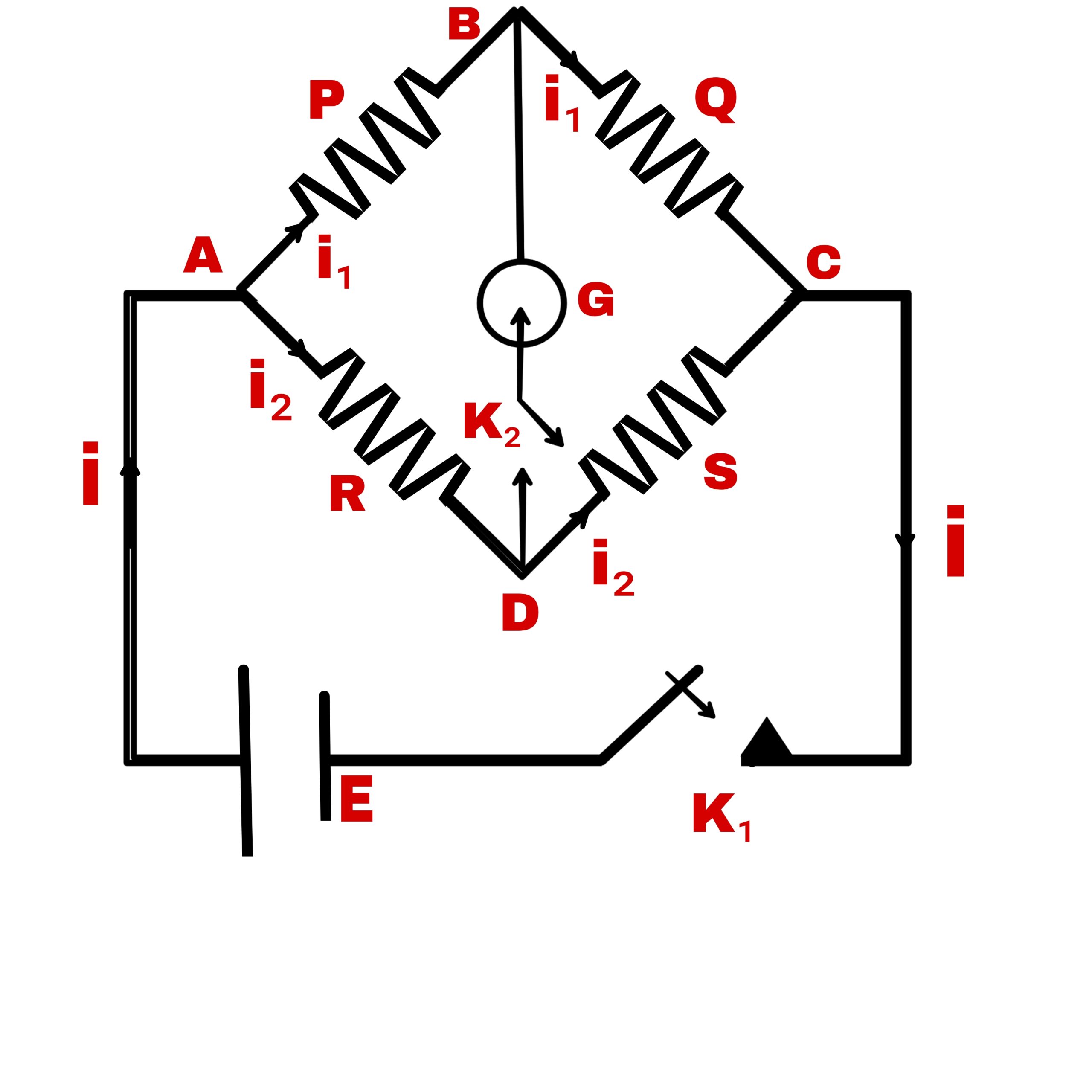
If four resistances are connected in series and represented by the four sides of a parallelogram and one diagonal of the quadrilateral is connected to the galvanometer and the other diagonal to the electric cell, if there is no declination in the galvanometer G, then,
P/Q=R/S
Proof —
Working
Suppose four resistances P, Q,R and S are connected as four arms of the quadrilateral ABCD. The galvanometer is connected on one side b/w points B & D and the electric cell is connected b/w A & C. There are two keys K₁ and K₂. Current i is passed through the electric cell E.
At point A, the current is divide into two parts, the one part i₁ flows in side AB and the other part i₂ flows in the side AD.
The resistance PQRS is adjusted in such a way that no the current flows in the galvanometer G on pressing the key K₂.
In this case, the current in the arm BC will be i₁, & the current in the arm DC will be i₂.
Kirchhoff’s second law for closed loop ABDA
i₁p – i₂R = 0
i₁p = i₂R ———-(1)
For closed loop BCDB
i₁Q – i₂S =0
i₁Q = i₂S ———-(2)
Equation (½)
(i₁p/i₁Q) = (i₂R/i₂S)
P/Q = R/S