Refraction of light
When a ray of light enters from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, it deviates from its straight path, this phenomenon is called refraction of light.
Or,
When a ray of light enters from a rarer medium to a denser medium, it bends towards the normal. Similarly, when a ray of light enters from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it deviates away from the normal, which we call refraction of light.
(Dense = dense, rarer = less dense)
Law of refraction
This rule is also called Snell’s law.
Snell propounded the following laws of refraction through experiments:
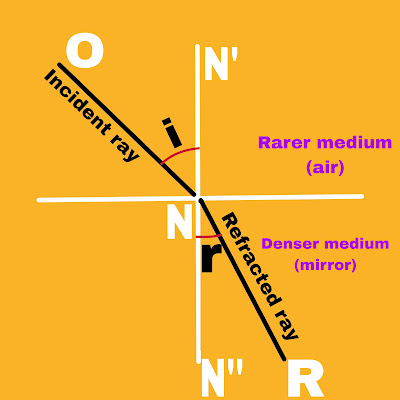
1. The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the refracting surface at the point of incidence, all three lie in the same plane.
2. For any transparent medium pair, the ratio of sine of the angle of incidence and sine of the angle of refraction is a constant.
The angle of incidence (i) and angle of refraction (r) are the angles that the incident ray and the refracted ray make with the normal respectively.
Therefore,
Refractive index of a medium =
Speed of light in vacuum/speed of light in medium
n = sin i / sin r
Where,
n is a constant, which is called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.