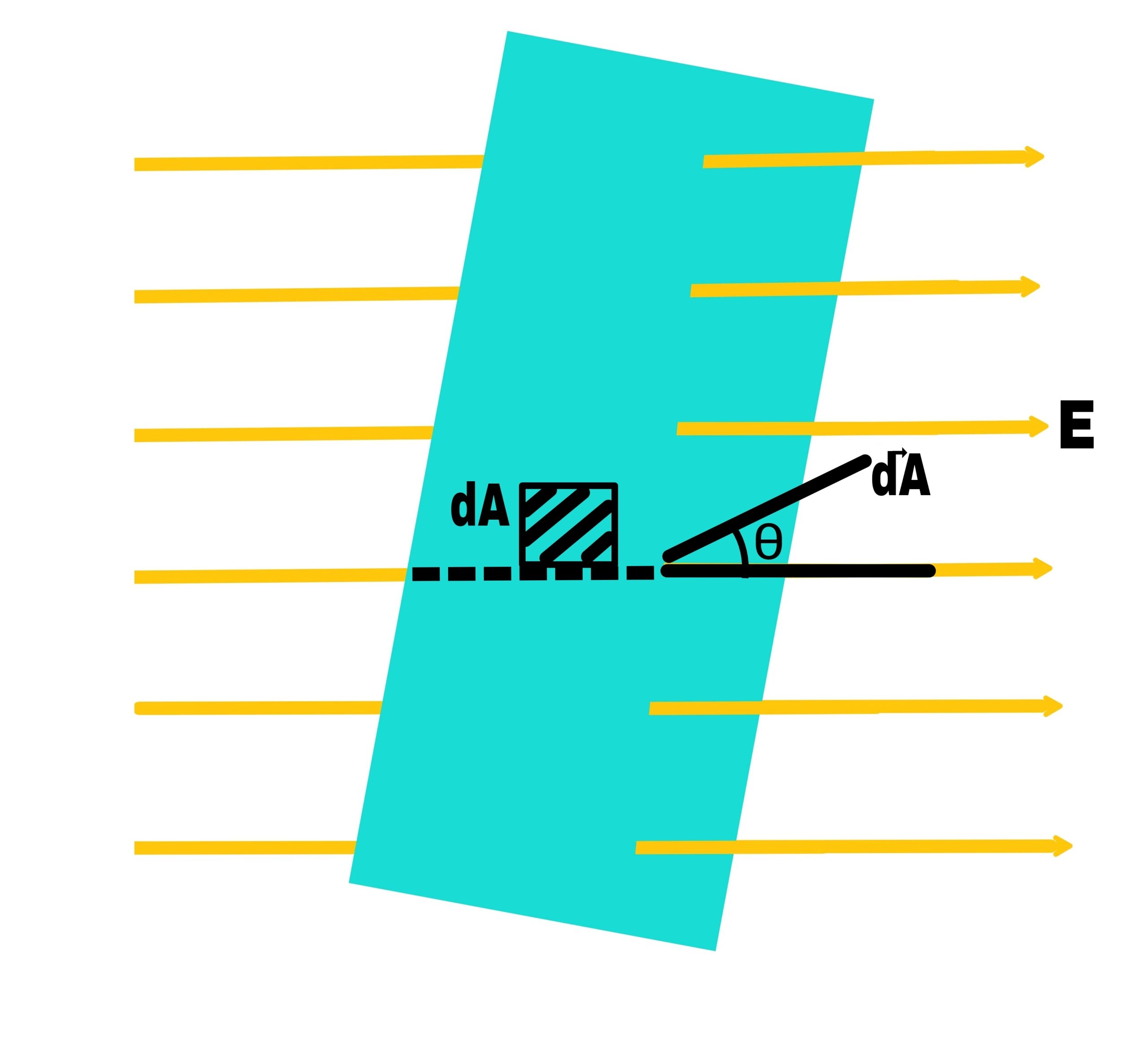
Electric flux
The number of the magnetic lines of force passing through a surface is called as electric flux. That is,
Electric flux is the measure of the number of magnetic lines of force passing through a surface and it represents the intensity of the electric field as a ratio of the number of electric lines of force.
Let the electric field at the position of surface element dA be E.
Hence,
The electric flux is mathematically defined as follows.
dΦₑ =→E.d→A
Electric flux with respect to the whole surface
or,
dΦₑ=∫ₐ→E.d→A
Φₑ= →E.→A
Φₑ=E.A.Cosθ
Φₑ=0
Case 1
When, θ= 0°
Φₑ=E.A.Cos0°
Φₑ=E.A
In this case the plane surface is normal to the electric field E.
Case 2
When,θ=90°
Φₑ=E.A.Cos90°
Φₑ=0
In this case the plane surface is parallel to the electric field E.
Unit and dimension of electric flux-
Φₑ=E.A
Φₑ=(Newton/Coulomb).meter²
Φₑ=Newton.Coulomb⁻¹.meter²
Φₑ=NC⁻¹M²
Dimensions
Φₑ=[MLT⁻²(AT)⁻¹L²]
Φₑ=[ML³T⁻³A⁻¹]