It is represented by ρ.
When electric current is impressed in conductor, then ratio of current density i in a conductor and intensity of the electric field is called the specific resistance or resistivity of the conductor.
Hence,
ρ = E/j
If the potential difference between the ends of the conductor is v and the current flowing in the conductor is i, then the intensity of electric field
E = v/l
Wherel = length of the conductor
j = i/A = current density
A = area of the conductor
Hence,
Specific resistance
ρ = E/j
ρ = [v/l]/[i/A]
ρ = [v/i].[l/A]
ρ = R.A/l
Where R = electrical resistance
Unit
Ohm.meter
Adjustment of resistance
1. Series combination
Suppose,
Three resistances R₁, R₂, and R₃ connected in a series respectively, the resultant resistance is R.
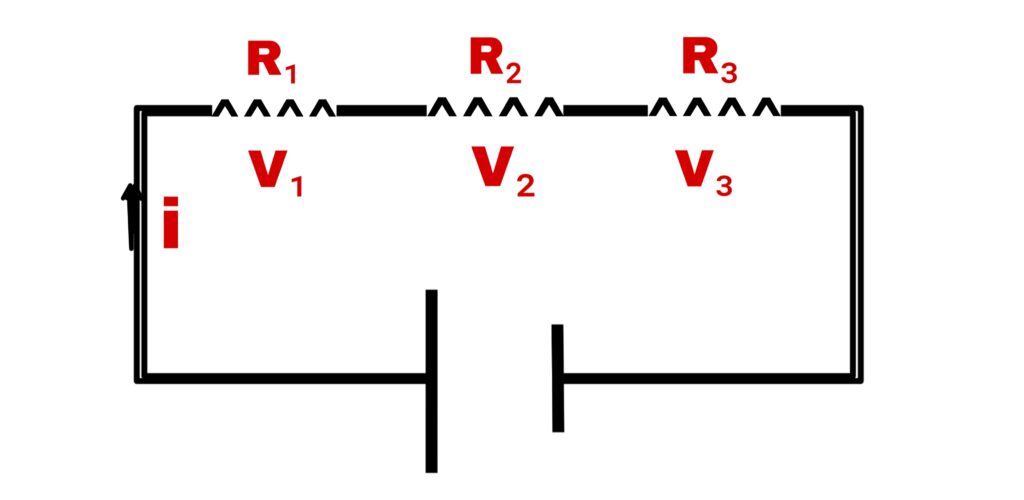
Three resistances connected in series so current through each resistance will be same.
V = V₁+V₂+V₃
iR =iR₁+iR₂+iR₃
R = R₁+R₂+R₃
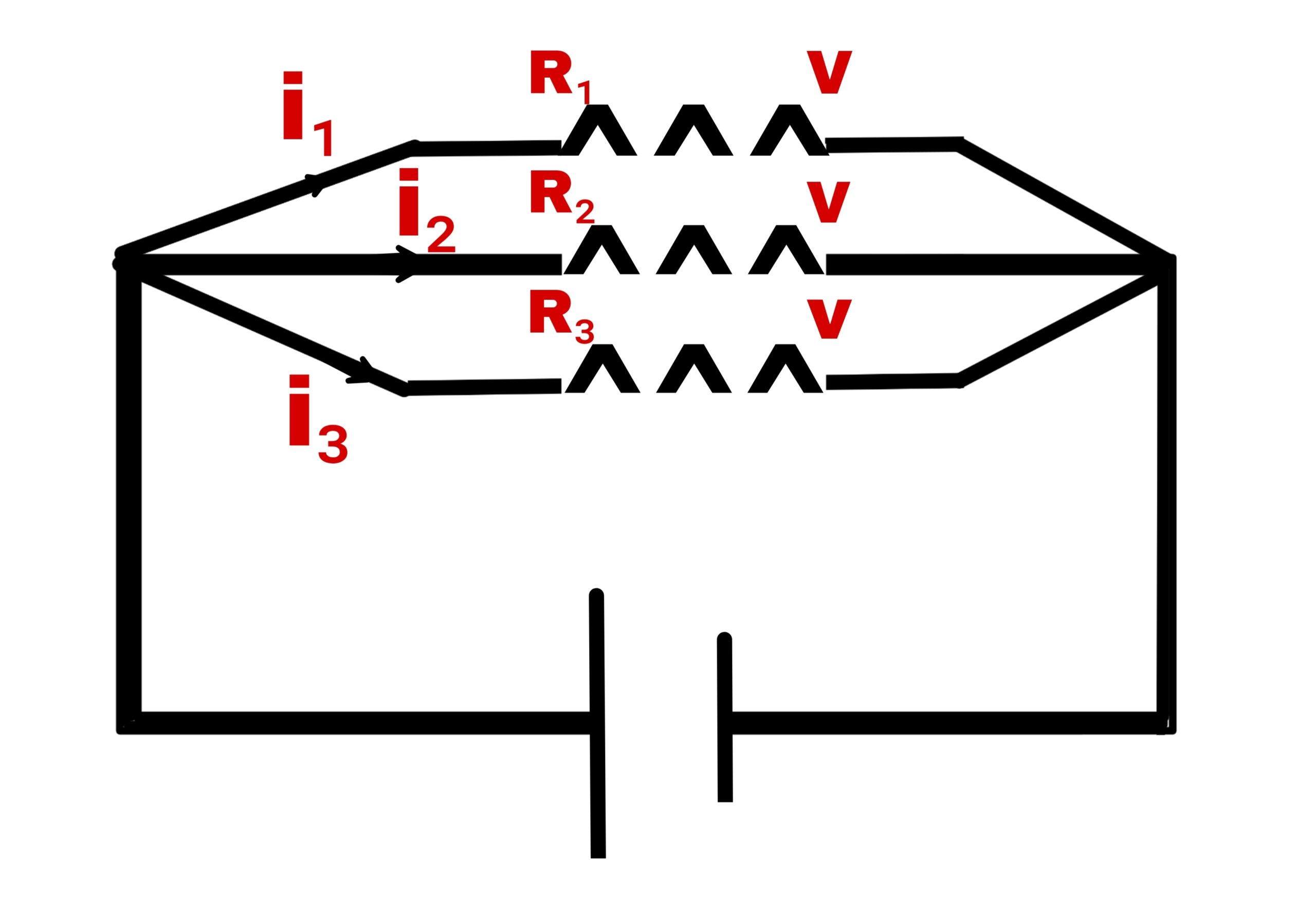
2. Parallel combination
In this type of combination each resistance has same potential difference.
Suppose three resistances R₁+R₂+R₃ connected in series and their resultant is R.
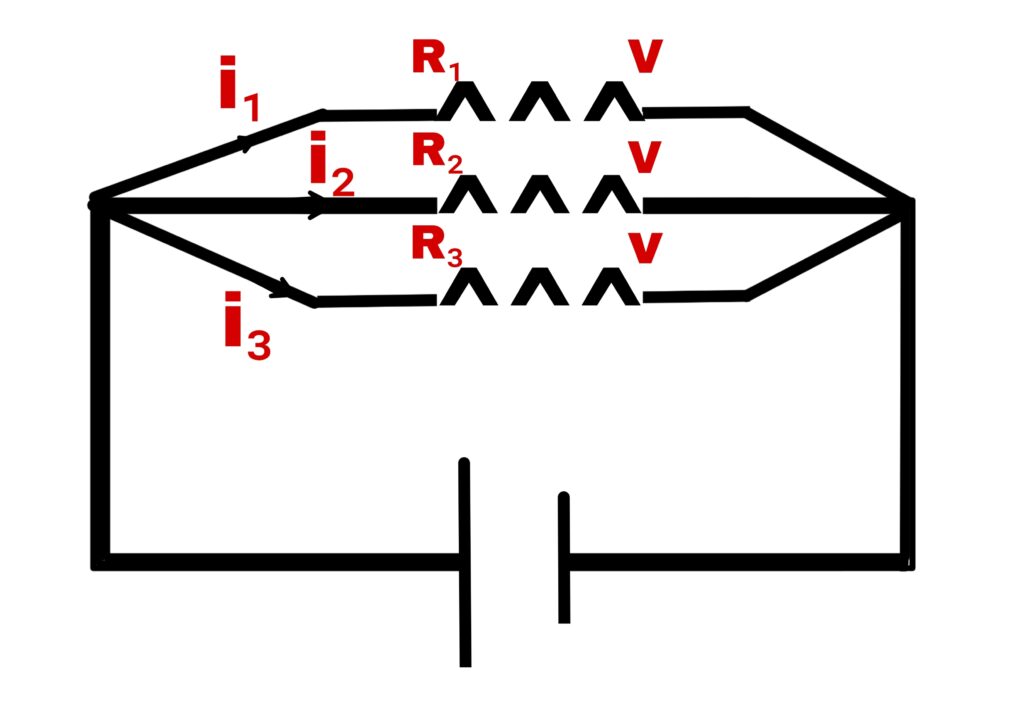
Hence resultant current
i = i₁+i₂+i₃
By Ohm’s law
V/R = V/R₁+V/R₂+V/R₃
1/R = 1/R₁+1/R₂+1/R₃